A novel, noninvasive assay shows that distal airway oxygen tension is low in cystic fibrosis, but not in primary ciliary dyskinesia
Leave a CommentAbstract
Objectives
Oxygen tension affects the biology of aerobic and denitrifying organisms. Using a novel, fast‐response sensor, we developed a noninvasive procedure to measure pO2 in distal human airways. We hypothesized that distal pO2 would be low in cystic fibrosis (CF) airways.

Materials and Methods
We measured the fraction of expired oxygen (FEO2) in real time using a fast laser diode analyzer in healthy subjects and in patients with CF, asthma, and primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD). Subjects slowly exhaled to residual volume (RV), where the nadir of FEO2 (NFO) was recorded. Values were compared to peripheral oxygen saturation (SaO2), expired CO2 at RV, FEV1, FEV1/FVC, and FEF25‐75. We also measured the effect of supplemental oxygen on FEO2.
Results
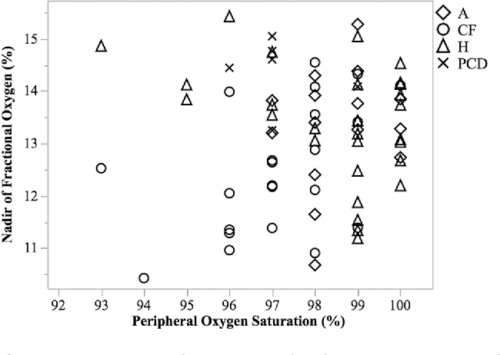
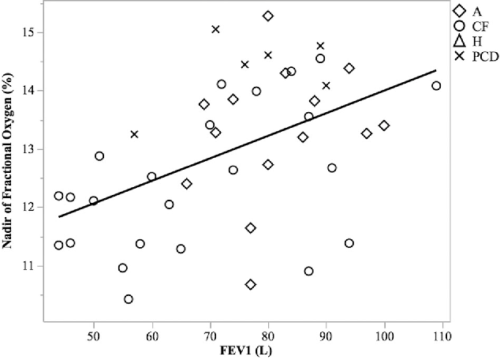
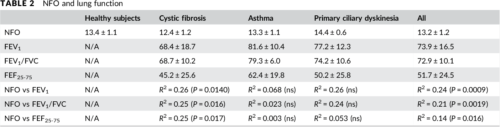
Seventy‐four subjects completed the study. Seven additional subjects could not perform the maneuver. Mean (±SD) NFO values for controls (n = 29), CF patients (n = 23), asthma patients (n = 15), and PCD patients (n = 7) were 13.4 ± 1.1%, 12.4 ± 1.2%, 13.3 ± 1.1%, 14.4 ± 0.6%, respectively. NFO in CF was lower than in controls (P = 0.0162), and NFO in PCD was higher than in CF (P = 0.0007). Asthma results were heterogeneous. Oxygen caused a dose‐dependent increase in NFO (P < 0.0005; n = 3; r2 = 0.91). NFO values were positively associated with FEV1 (P = 0.0009), FEV1/FVC (P = 0.0019) and FEF25‐75 (P = 0.0155), but there was no association with SaO2.
Conclusions
Distal airway pO2 is lower in CF than in controls. This may reflect absorption of oxygen in partially plugged acinar units, and/or increased epithelial oxygen consumption. Distal airway pO2 can be precisely titrated to treat infections.
First published: 28 November 2018; Pediatric Pulmonology
A novel, noninvasive assay shows that distal airway oxygen tension is low in cystic fibrosis, but not in primary ciliary dyskinesia (pdf)
Mechanical ventilators in the hot zone: Effects of a CBRN filter on patient protection and battery life
Leave a CommentAbstract
Objective
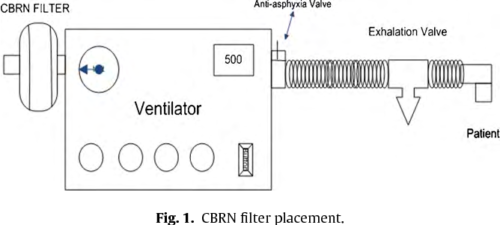
In a contaminated environment, respiratory protection for ventilator dependent patients can be achieved by attaching a chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear (CBRN) filter to the air intake port of a portable ventilator. We evaluated the effect of the filter on battery performance of four portable ventilators in a laboratory setting.
Methods
Each ventilator was attached to a test lung. Ventilator settings were: assist control (AC) mode, respiratory rate 35 bpm, tidal volume 450 ml, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 10 cm H2O, inspiratory time 0.8 s, and FIO2 0.21. Ventilators were operated until the battery was fully discharged. We also evaluated the ventilators’ ability to deliver all the gas through the CBRN filter and analyzed the pressures required to breathe through the anti-asphyxiation valve of a failed device.
Results
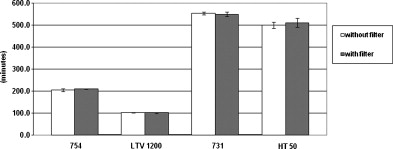
The range of battery life varied widely across different ventilator models (99.8–562.6 min). There was no significant difference in battery life (p < 0.01) when operating with or without the CBRN filter attached. Only the Impact 731 routed all inspired gases through the CBRN filter. The pressure required to breathe though the failed device was −4 cm H2O to −9 cm H2O.
Conclusions
Duration of operation from the internal battery was not altered by attachment of the CBRN filter. The use of a CBRN filter is necessary for protection of ventilator dependent patients when environmental contamination is present, although conditions exist where all gas does not pass through the filter with some ventilators under normal operating conditions.
in Resuscitation 81(9):1148-51 · September 2010
Authors: Thomas C. Blakeman (a) , Peter Toth (c), Dario Rodriquez (b), Richard D. Branson (a)
(a) University of Cincinnati Department of Surgery, Division of Trauma/Critical Care, Cincinnati, OH, United States
(b) Center for Sustainment of Trauma and Readiness Skills (CSTARS), United States Air Force, Cincinnati, OH, United States
(c) Medical Student, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, United States
Mechanical ventilators in the hot zone: Effects of a CBRN filter on patient protection and battery life (pdf)
President’s Day Holidays
Leave a CommentOxigraf Offices will be closed for President’s Day on February 17, 2020.
CPET – Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing
Leave a CommentA cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET) is an evaluation of the cardiopulmonary system.
Physical exercise requires the interaction of the physiologic mechanisms that enable the cardiovascular and respiratory systems to support the energy demands of the contracting muscles. Both systems are consequently stressed during exercise. Their ability to respond adequately to this stress is a measure of their physiologic competence.
- Studies are performed under the direction of the cardiology and pulmonary divisions
- Emphasis of testing may be influenced by the requesting division
- Cardiac patients have more detailed electrocardiogram (ECG)/hemodynamic monitoring during testing
- Pulmonary patient studies may include bronchial provocation with exercise testing
- Exercise modalities
- Bicycle ergometer
- Treadmill
- Selection of modality and protocol are dependent upon the requesting physician, level of fitness and health, weight, age, and patient preference
Model O2CPX – Cardiopulmonary Exercise Analyzer
The Model O2CPX is a table top analyzer used to monitor performance parameters during exercise testing. Breath-by-breath O2, CO2 and flow rate is measured precisely and accurately with internal sensors. Heart rate and pulse oximetry interfaces are compatible with Polar and Nonin accessories. Ambient temperature, humidity and barometric pressure is acquired for precise measurement correction. Our reliable solid state oxygen sensor does not require routine maintenance or factory calibration. Our O2CPX hardware easily collaborates with customer software solutions via USB interface.
KONA Software Designed for The Model O2CPX
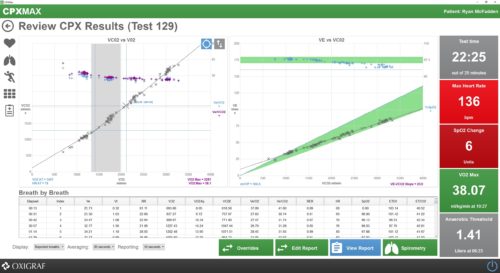
Next generation cardiopulmonary exercise testing screen, with interactive breath-by-breath validation:
- Visual test results viewer with custom charts and tabular breath-by-breath view.
- Automatic VO2 and anaerobic thresholds can be manually overridden.
- Custom reports including charts and key metrics.
- FVC spirometry comparison test and pre/post FVCcomparison test.
- Spirometry reports can be generated independently.
- Patient management section with demographic information.
- Easy calibrate screen. Pneumotachs are easily calibrated by entering a quick code.
- Automatic flow volume correction using built in, temperature, humidity and barometric pressure sensors.
- Oxygen saturation and polar heart rate input.
- Optional ECG stress-test integration.
- Optional multi-node test site version with shared relational database engine and support for 25+ test and review stations
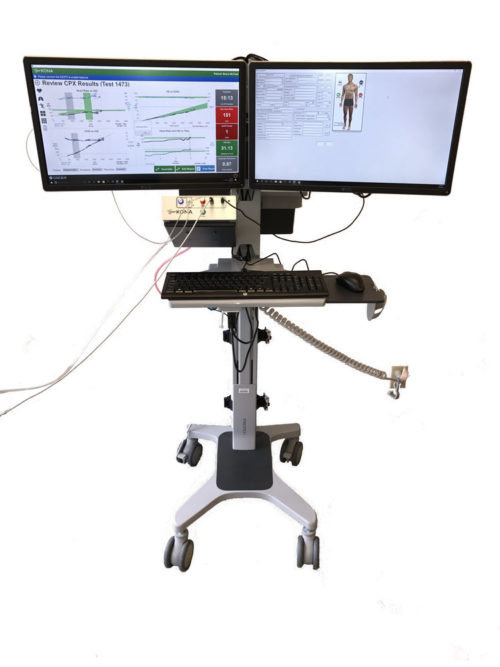

Ergotron System Cart
Ergotron Neo-flex computer cart with height adjustable monitor and work surface for standing and sitting situations.
Complete systems cart configuration with mounting for
- Oxigraf Model O2CPX Cardio-Pulmonary Exercise Test Analyzer mounting
- Single monitor (up to 42 inch) or dual monitor mounting for 22 inch displays
- Keyboard and Mouse work surface
- Integrated Intel NUC computer mounting
- Integrated power and cable routing
- Mounting for 500L calibration gas cylinder on rear
Please download your O2CPX analyzer brochure.
Please download your KONA Software brochure.
Please download your Ergotron Cart brochure.